# How Is Dew Point Calculated?
Understanding Dew Point
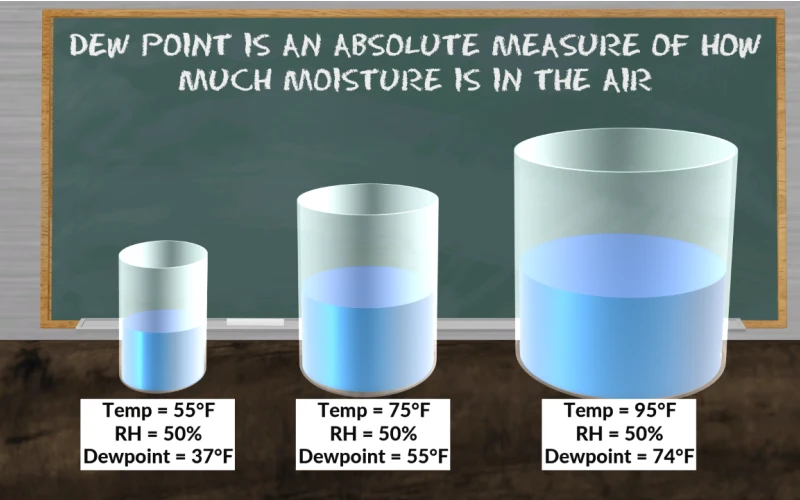
Dew point is a crucial meteorological concept that indicates the temperature at which air becomes saturated with water vapor, leading to the formation of dew. Understanding how dew point is calculated helps in predicting weather conditions, especially humidity-related phenomena.
The Basic Formula for Dew Point Calculation
The most commonly used method to calculate dew point is the Magnus-Tetens formula, which provides a close approximation based on temperature and relative humidity. The formula is as follows:
Td = (b × α(T, RH)) / (a – α(T, RH))
Where:
- Td is the dew point temperature in °C.
- T is the air temperature in °C.
- RH is the relative humidity in percentage (%).
- a and b are constants: a = 17.27 and b = 237.7 °C.
- α(T, RH) is calculated as: α(T, RH) = (a × T) / (b + T) + ln(RH/100).
Step-by-Step Calculation
To calculate the dew point using the Magnus-Tetens formula, follow these steps:
- Convert the relative humidity (RH) from a percentage to a decimal by dividing by 100.
- Calculate the intermediate value α(T, RH) using the formula: α(T, RH) = (17.27 × T) / (237.7 + T) + ln(RH).
- Plug the value of α(T, RH) into the dew point formula: Td = (237.7 × α(T, RH)) / (17.27 – α(T, RH)).
Example Calculation
Let’s say the air temperature (T) is 25°C, and the relative humidity (RH) is 60%:
- Convert RH to decimal: 60% → 0.60.
- Calculate α(T, RH): (17.27 × 25) / (237.7 + 25) + ln(0.60) ≈ 1.313.
- Calculate Td: (237.7 × 1.313) / (17.27 – 1.313) ≈ 16.7°C.
Thus, the dew point temperature is approximately 16.7°C.
Alternative Methods
While the Magnus-Tetens formula is widely used, other methods and empirical equations can also calculate dew point, such as the Arden Buck equation or using psychrometric charts. These methods may offer higher accuracy under specific conditions.
Why Dew Point Matters
Dew point is a valuable indicator in weather forecasting, agriculture, and HVAC systems. A higher dew point suggests more moisture in the air, which can lead to discomfort, fog, or even thunderstorms. Conversely, a low dew point indicates dry air, which is common in arid climates.
By understanding how dew point
Keyword: how is dew point calculated